浅析线程本地存储--ThreadLocal
2019, Aug 09
一、为什么会有线程本地存储?
在实现线程安全时,有一种策略是无同步方案。
如果一段代码中所需要的数据必须与其他代码共享,那就看看这些共享数据的代码是否能保证在同一个线程中执行。如果能保证,我们就可以把共享数据的可见范围限制在同一个线程之内,这样,无须同步也能保证线程之间不出现数据争用的问题。
由此就有了线程本地存储的使用场景。
二、ThreadLocal 使用
public class Test {
public static ThreadLocal<Integer> tl = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static CopyOnWriteArrayList<Integer> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new MyThread(1);
Thread t2 = new MyThread(2);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
static class MyThread extends Thread{
Integer value;
public MyThread(Integer value){
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public void run(){
setValue();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
printValue();
}
private void setValue(){
System.out.println("setValue......");
tl.set(value);
list.add(0,value);
}
private void printValue(){
System.out.println("ThreadLocal "+Thread.currentThread()+" "+tl.get());
System.out.println("List "+Thread.currentThread()+" "+list.get(0));
}
}
}
输出为
setValue......
setValue......
ThreadLocal Thread[Thread-1,5,main] 2
ThreadLocal Thread[Thread-0,5,main] 1
List Thread[Thread-0,5,main] 2
List Thread[Thread-1,5,main] 2
通过与线程共享的List对比,可以看到,ThreadLocal中持有的对象是基于每线程的。
三、分析源码
ThreadLocal中的set方法:
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
从getMap()点进去:
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
可以看到,每个线程有一个threadLocalMap。看代码好像不是很清晰,看下图就很好懂了
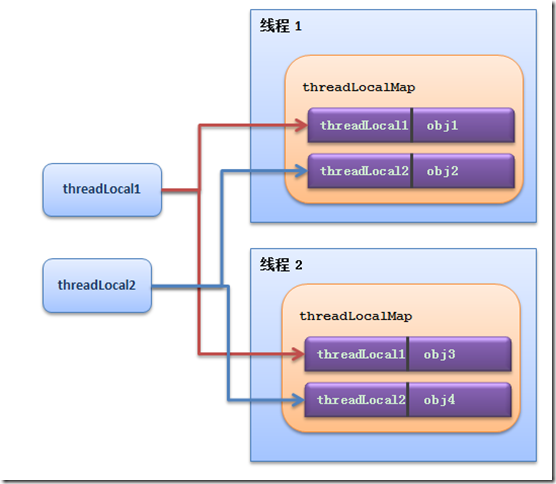
同理,对于get方法,也是先获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap,然后以调用get的当前ThreadLocal为key,获取到持有的Object。
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
总结
每个线程有一个ThreadLocalMap,新建一个ThreadLocal并set一个value时,会把这个ThreaLocal作为key,value作为值存到当前线程的ThreadLocalMap中。
简单的分析,如有错漏之处,希望海涵并不吝赐教!